货号
产品规格
售价
备注
BN41938R-50ul
50ul
¥1486.00
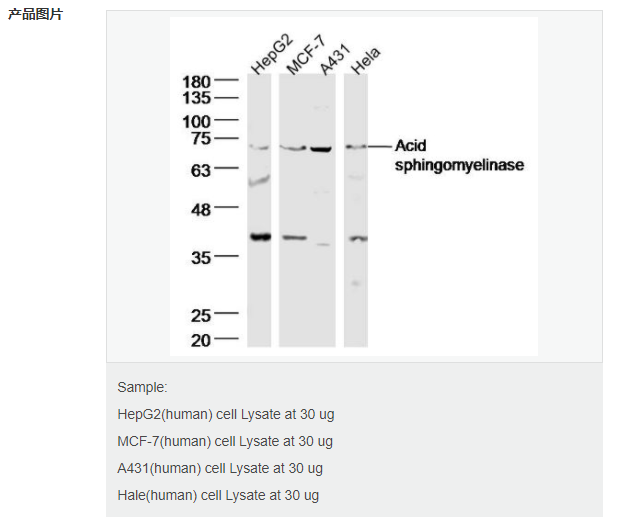
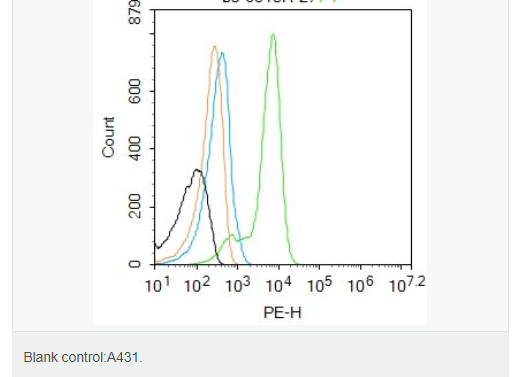
交叉反应:Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Rabbit) 推荐应用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41938R-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
交叉反应:Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Rabbit) 推荐应用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41938R-200ul
200ul
¥3490.00
交叉反应:Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Rabbit) 推荐应用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
| 英文名称 | Acid sphingomyelinase |
| 中文名称 | 酸性神经鞘磷脂酶抗体 |
| 别 名 | Acid sphingomyelinase; ASM; ASM_HUMAN; aSMase; NPD; Smpd1; Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1 acid lysosomal; Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase. |
| 研究领域 | 细胞生物 神经生物学 信号转导 细胞凋亡 |
| 抗体来源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆类型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反应 | Human, Mouse, Rat, (predicted: Dog, Pig, Cow, Rabbit, ) |
| 产品应用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 Flow-Cyt=2ug/Test ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蜡切片需做抗原修复) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 64kDa |
| 细胞定位 | 细胞浆 |
| 性 状 | Liquid |
| 浓 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Acid sphingomyelinase:201-300/629 |
| 亚 型 | IgG |
| 纯化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 储 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存条件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 产品介绍 | Converts sphingomyelin to ceramide. Also has phospholipase C activities toward 1,2-diacylglycerolphosphocholine and 1,2-diacylglycerolphosphoglycerol. Isoform 2 and isoform 3 have lost catalytic activity. Involvement in disease: Defects in SMPD1 are the cause of Niemann-Pick disease type A (NPDA) ; also known as Niemann-Pick disease classical infantile form. It is an early-onset lysosomal storage disorder caused by failure to hydrolyze sphingomyelin to ceramide. It results in the accumulation of sphingomyelin and other metabolically related lipids in reticuloendothelial and other cell types throughout the body, leading to cell death. Niemann-Pick disease type A is a primarily neurodegenerative disorder characterized by onset within the first year of life, mental retardation, digestive disorders, failure to thrive, major hepatosplenomegaly, and severe neurologic symptoms. The severe neurological disorders and pulmonary infections lead to an early death, often around the age of four. Clinical features are variable. A phenotypic continuum exists between type A (basic neurovisceral) and type B (purely visceral) forms of Niemann-Pick disease, and the intermediate types encompass a cluster of variants combining clinical features of both types A and B. Function: Converts sphingomyelin to ceramide. Also has phospholipase C activities toward 1,2-diacylglycerolphosphocholine and 1,2-diacylglycerolphosphoglycerol. Isoform 2 and isoform 3 have lost catalytic activity. Subunit: Monomer. Subcellular Location: Lysosome. DISEASE: Defects in SMPD1 are the cause of Niemann-Pick disease type A (NPDA) [MIM:257200]; also known as Niemann-Pick disease classical infantile form. It is an early-onset lysosomal storage disorder caused by failure to hydrolyze sphingomyelin to ceramide. It results in the accumulation of sphingomyelin and other metabolically related lipids in reticuloendothelial and other cell types throughout the body, leading to cell death. Niemann-Pick disease type A is a primarily neurodegenerative disorder characterized by onset within the first year of life, mental retardation, digestive disorders, failure to thrive, major hepatosplenomegaly, and severe neurologic symptoms. The severe neurological disorders and pulmonary infections lead to an early death, often around the age of four. Clinical features are variable. A phenotypic continuum exists between type A (basic neurovisceral) and type B (purely visceral) forms of Niemann-Pick disease, and the intermediate types encompass a cluster of variants combining clinical features of both types A and B. Defects in SMPD1 are the cause of Niemann-Pick disease type B (NPDB) [MIM:607616]; also known as Niemann-Pick disease visceral form. It is a late-onset lysosomal storage disorder caused by failure to hydrolyze sphingomyelin to ceramide. It results in the accumulation of sphingomyelin and other metabolically related lipids in reticuloendothelial and other cell types throughout the body, leading to cell death. Clinical signs involve only visceral organs. The most constant sign is hepatosplenomegaly which can be associated with pulmonary symptoms. Patients remain free of neurologic manifestations. However, a phenotypic continuum exists between type A (basic neurovisceral) and type B (purely visceral) forms of Niemann-Pick disease, and the intermediate types encompass a cluster of variants combining clinical features of both types A and B. In Niemann-Pick disease type B, onset of the first symptoms occurs in early childhood and patients can survive into adulthood. Similarity: Belongs to the acid sphingomyelinase family. Contains 1 saposin B-type domain. SWISS: P17405 Gene ID: 6609 Database links: Entrez Gene: 100720041 Guinea pig Entrez Gene: 6609 Human Entrez Gene: 20597 Mouse Entrez Gene: 100353898 Rabbit Omim: 607608 Human SwissProt: P17405 Human SwissProt: Q04519 Mouse Unigene: 498173 Human Unigene: 4628 Mouse Unigene: 485064 Mouse Unigene: 18277 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. ASM酸性神经鞘磷脂酶是ASMase神经鞘磷脂酶最重要的一个亚型,是细胞膜的重要组成成分。ASM在细胞凋亡、调节肿瘤细胞生长、参与Fas信号系统传递等方面均可发挥重要作用。 |