货号
产品规格
售价
备注
BN41848R-50ul
50ul
¥1486.00
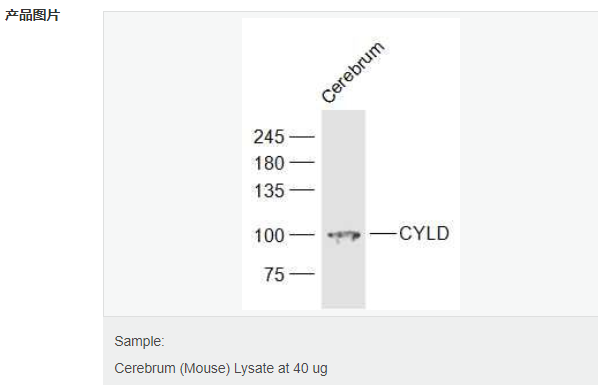
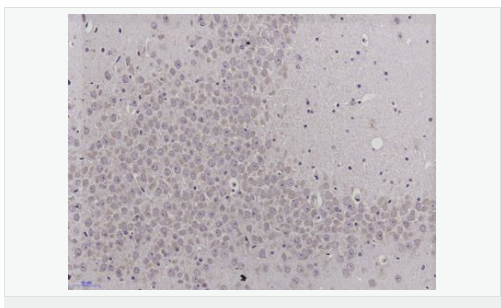
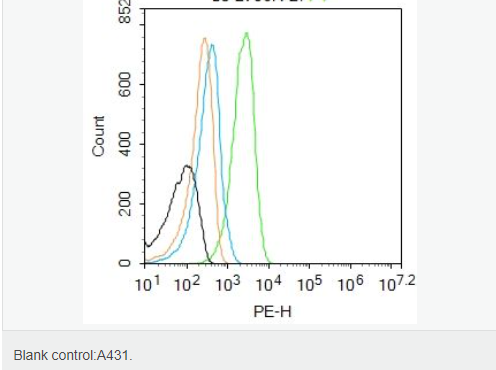
交叉反应:Rat,Mouse,Human(predicted:Horse,Cow,Chicken) 推荐应用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41848R-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
交叉反应:Rat,Mouse,Human(predicted:Horse,Cow,Chicken) 推荐应用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41848R-200ul
200ul
¥3490.00
交叉反应:Rat,Mouse,Human(predicted:Horse,Cow,Chicken) 推荐应用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
| 英文名称 | CYLD |
| 中文名称 | 微管结合蛋白CYLD抗体 |
| 别 名 | CDMT; cylindromatosis (turban tumor syndrome); cylindromatosis 1; Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD; EAC; HSPC057; KIAA0849; turban tumor syndrome; Ubiquitin thiolesterase CYLD; Ubiquitin-specific processing protease CYLD; CYLD_HUMAN; Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase CYLD; CYLD; BRSS; CDMT; CYLD1; CYLDI; EAC; MFT; MFT1; SBS; TEM; USPL2. |
| 研究领域 | 肿瘤 细胞生物 |
| 抗体来源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆类型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反应 | Human, Mouse, Rat, (predicted: Chicken, Cow, Horse, ) |
| 产品应用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 Flow-Cyt=2ug/Test IF=1:100-500 (石蜡切片需做抗原修复) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 105kDa |
| 细胞定位 | 细胞浆 细胞膜 |
| 性 状 | Liquid |
| 浓 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human cylindromatosis 1:501-600/956 |
| 亚 型 | IgG |
| 纯化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 储 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存条件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 产品介绍 | Defects in CYLD are the cause of familial cylindromatosis (CYLD) also known as turban tumor syndrome or dermal eccrine cylindromatosis. CYLD is an autosomal dominant and highly tumor type-specific disorder. The tumors (known as cylindromas because of their characteristic microscopic architecture) are believed to arise from or recapitulate the appearance of the eccrine or apocrine cells of the skin that secrete sweat and scent respectively. Cylindromas arise predominantly in hairy parts of the body with approximately 90% on the head and neck. The development of a confluent mass which may ulcerate or become infected has led to the designation "turban tumor syndrome". The skin tumors show differentiation in the direction of hair structures, hence the synonym trichoepithelioma. CYLD has deubiquitinating activity. Function: Protease that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains. Has endodeubiquitinase activity. Plays an important role in the regulation of pathways leading to NF-kappa-B activation. Contributes to the regulation of cell survival, proliferation and differentiation via its effects on NF-kappa-B activation. Negative regulator of Wnt signaling. Inhibits HDAC6 and thereby promotes acetylation of alpha-tubulin and stabilization of microtubules. Plays a role in the regulation of microtubule dynamics, and thereby contributes to the regulation of cell proliferation, cell polarization, cell migration, and angiogenesis. Required for normal cell cycle progress and normal cytokinesis. Inhibits nuclear translocation of NF-kappa-B. Plays a role in the regulation of inflammation and the innate immune response, via its effects on NF-kappa-B activation. Dispensable for the maturation of intrathymic natural killer cells, but required for the continued survival of immature natural killer cells. Negatively regulates TNFRSF11A signaling and osteoclastogenesis Subunit: Interacts (via CAP-Gly domain) with IKBKG/NEMO (via proline-rich C-terminal region). Interacts with TRAF2 and TRIP. Interacts with PLK1, DVL1, DVL3, MAVS, TBK1, IKKE and DDX58. Interacts (via CAP-Gly domain) with microtubules. Interacts with HDAC6 and BCL3. Interacts with SQSTM1 and MAP3K7. Identified in a complex with TRAF6 and SQSTM1. Subcellular Location: Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Note=Detected at the microtubule cytoskeleton during interphase. Detected at the midbody during telophase. Tissue Specificity: Detected in fetal brain, testis, and skeletal muscle, and at a lower level in adult brain, leukocytes, liver, heart, kidney, spleen, ovary and lung. Isoform 2 is found in all tissues except kidney. Post-translational modifications: Phosphorylated on several serine residues by IKKA and/or IKKB in response to immune stimuli. Phosphorylation requires IKBKG. Phosphorylation abolishes TRAF2 deubiquitination, interferes with the activation of Jun kinases, and strongly reduces CD40-dependent gene activation by NF-kappa-B. DISEASE: Familial cylindromatosis (FCYL) [MIM:132700]: Autosomal dominant and highly tumor type-specific disorder. The tumors (known as cylindromas because of their characteristic microscopic architecture) are believed to arise from or recapitulate the appearance of the eccrine or apocrine cells of the skin that secrete sweat and scent respectively. Cylindromas arise predominantly in hairy parts of the body with approximately 90% on the head and neck. The development of a confluent mass which may ulcerate or become infected has led to the designation 'turban tumor syndrome'. The skin tumors show differentiation in the direction of hair structures, hence the synonym trichoepithelioma. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Multiple familial trichoepithelioma 1 (MFT1) [MIM:601606]: Autosomal dominant dermatosis characterized by the presence of many skin tumors predominantly on the face. Since histologic examination shows dermal aggregates of basaloid cells with connection to or differentiation toward hair follicles, this disorder has been thought to represent a benign hamartoma of the pilosebaceous apparatus. Trichoepitheliomas can degenerate into basal cell carcinoma. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Brooke-Spiegler syndrome (BRSS) [MIM:605041]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the appearance of multiple skin appendage tumors such as cylindroma, trichoepithelioma, and spiradenoma. These tumors are typically located in the head and neck region, appear in early adulthood, and gradually increase in size and number throughout life. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Similarity: Belongs to the peptidase C67 family. Contains 3 CAP-Gly domains. SWISS: Q9NQC7 Gene ID: 1540 Database links: Entrez Gene: 1540 Human Entrez Gene: 74256 Mouse Omim: 605018 Human SwissProt: Q9NQC7 Human SwissProt: Q80TQ2 Mouse Unigene: 578973 Human Unigene: 482446 Mouse Unigene: 128760 Rat Unigene: 168938 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. CYLD(cylindromatosis)是近年发现的一种肿瘤抑制基因,CYLD丢失或突变可致肿瘤形成,多个研究显示,其表达蛋白CYLD可去泛素化TRAFs、NEMO、Bcl-3及p53等信号分子,调控细胞NF-κB和JNK等信号途径,CYLD在人体内广泛分布,在细胞周期的调控、介导细胞凋亡、抑制肿瘤发生等分子事件中有着重要的调控作用。 CYLD基因缺陷或缺失主要导致头部或面部的皮肤肿瘤,如多发性家族性毛发上皮瘤(MFT),家族性圆柱瘤(FC)和Brooke-Spiegler综合症(BSS),此外,CYLD在宫颈癌、肾癌、结肠癌、肝癌形成的信号途径中也均表现为下游调控,是目前用于肿瘤研究的热门抗体。 |